Understanding Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) in IVF
In the journey toward parenthood, several couples face unexpected challenges that require not only emotional resilience but also medical innovation.
One such advancement that is reshaping the landscape of assisted reproduction is Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT), a powerful tool used during In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) to increase the chances of a healthy pregnancy.
By allowing the best IVF doctors in India to screen embryos for genetic abnormalities before implantation, PGT provides hope, clarity and a more tailored approach to family planning.
Whether you are exploring IVF for the first time or curious to know about the technologies involved, this blog will guide you through the essentials of PGT.
Let’s get started.
What is PGT (Preimplantation Genetic Testing)?
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) is an advanced technique used to detect genetic abnormalities in embryos developed through in vitro fertilization (IVF). Its primary goal is to assist doctors in selecting embryos that are most likely free of specific genetic conditions or chromosomal issues for implantation. By doing so, PGT offers patients the chance to lower the risk of passing on genetic diseases to their future children before pregnancy begins.
How Does PGT Work?
The first step to PGT is to look for a trusted physician who provides infertility treatment in India and have a thorough discussion. Genetic counselling is also strongly recommended to understand both the benefits and limitations of the test. However, one thing to remember is that PGT should be planned ahead of your IVF cycle.
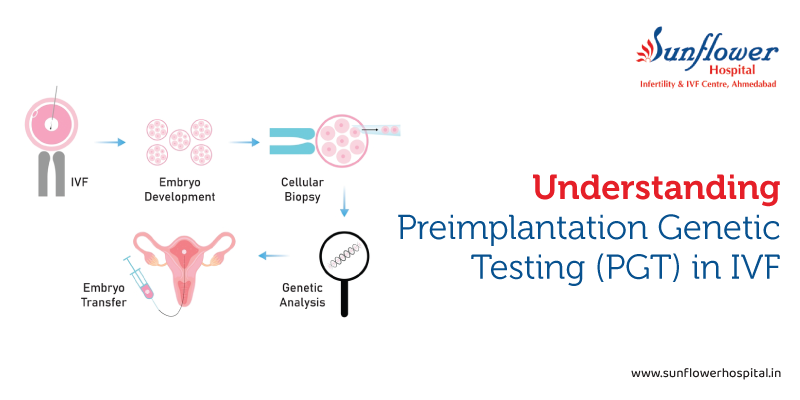
That’s because, during IVF, eggs are retrieved and fertilized to create embryos. On the fifth or sixth day, when embryos reach the blastocyst stage, a few cells are biopsied and sent to a reference lab for testing.
Meanwhile, the embryos are frozen and stored. After receiving the result, your doctor will discuss the findings, and if suitable embryos are available, you’ll schedule a frozen embryo transfer.
Screening to Prevent the Inheritance of a Single-Gene Disorder (PGT-M)
Some patients opt for IVF with PGT to reduce the likelihood of transmitting a specific genetic condition. This process is called PGT-M (Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Monogenic Disorders) and is typically recommended when one or both partners are carriers of inherited conditions such as cystic fibrosis or sickle cell anemia. In certain cases, families may also pursue HLA matching to find a compatible embryo for a child requiring a stem cell donor.
Screening of Chromosome Abnormalities (PGT-A and PGT-SR)
PGT testing can also assess an embryo’s chromosomes to check for abnormalities like missing or extra chromosomes, known as aneuploidy. These abnormalities are common and can lead to failed IVF cycles, miscarriage, or conditions like Down Syndrome.
While embryos are generally chosen based on appearance (grading), this method isn’t always reliable. PGT-A (preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy) offers accurate insight into an embryo’s potential, helping choose the best one for transfer. PGT-A is generally suggested for patients with recurrent miscarriages, multiple failed IVF attempts, prior chromosomal conditions, and more.
Another form of testing, PGT-SR (Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Structural Rearrangements), is recommended when a patient or their partner carries a structural chromosome abnormality, such as a translocation. This test detects embryos with missing or extra segments of chromosomes, helping to reduce the risk of miscarriage or severe health complications.
In the end, these are some of the things you need to understand about PGT (preimplantation genetic testing). However, you can consult an IVF specialist today if you want to get more information regarding PGT.
related blog
When to Visit a Male Fertility Specialist
Micro TESE Procedure Explained