Female Partner Examination
- Detailed History
- Clinical Examination
- Sonography
- Lab Investigation
- Karyotyping
- Plan Treatment Protocol
After a detailed history & physical examination, few basic laboratory investigations & a sonological evaluation is very important to choose the modality of treatment for infertility as it affects the success rate of the treatment.

sunflower success numbers
1500+
IVF and ICSI procedures a year.
22000+
Live births by IVF and ICSI technology.
Life member
AOGS, AICOG, FOGSI, ISAR, ESHRE, ASRM, IFFS, IMA.
Success rate
70% to 76% in IVF ART.
Clinical examination
We start the clinical examination of female by measuring her weight & height & then calculating her BMI. Our experience has shown that ladies who have normal BMI not only respond well to the treatment of infertility but also have a better outcome of pregnancy as compared to their obese or underweight counterparts.
After recording the weight, the lady should be escorted into a comfortable examination room by a trained nursing staff where detailed general & systemic examination is done. Verbal consent is obtained & procedure explained in detail. We need not stress that if male doctor should do the examination it will be in presence of a female nursing staff. During the examination findings of relevance are development of secondary sexual characters ( breasts, axillary and pubic hair) , presence or absence of galactorrhoea, signs of androgen excess like abnormal hair growth & thyroid enlargement. Sterile speculum examination is important to examine cervix and vagina for any abnormality of signs of infection and to rule out vaginismus from other causes of dyspareunia. Bimanual examination gives idea about the size & mobility of uterus. Any abnormal finding in physical examination should be supported by laboratory & radiological evidences & should be treated before the treatment of infertility commences.
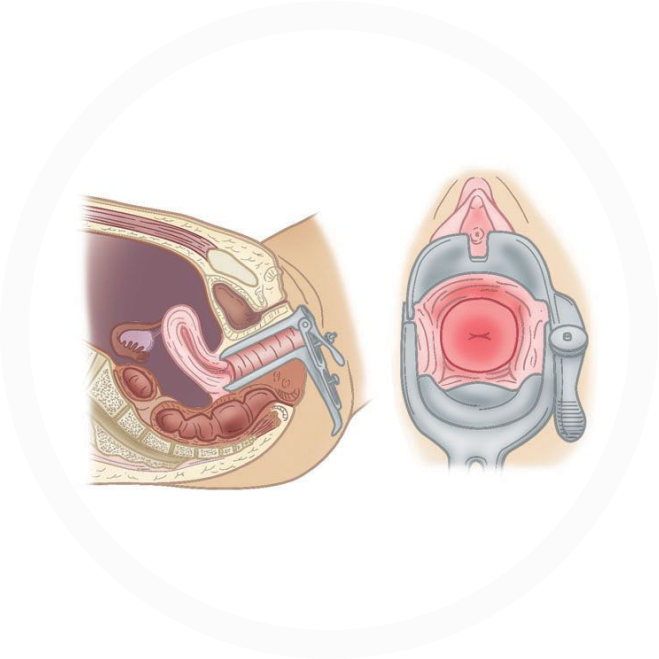
Ultrasonography
Transvaginal sonography with 3D evaluation of uterine cavity has become the most important tool in the armamentarium of the physician to diagnose & treat infertility. TVS has a high sensitivity & specificity for follicular monitoring, prediction & conformation of ovulation.
While evaluating the female genital system by TVS, the examiner should scan every part in detail.
Transvaginal ultrasound examination of the body of uterus is done to observe a detailed view of the myometrium & to diagnose any mullerian anomalies like septate uterus & bicornuate uterus , fibroid & adenomyosis.
Cervix is evaluated for the length of the cervix, nabothian cyst & Cervical Fibroid.
Endometrial cavity is scanned for endometrial thickness, endometrial pattern, endometrial polyps & presence of any foreign bodies or synechia, endometrial blood flow.
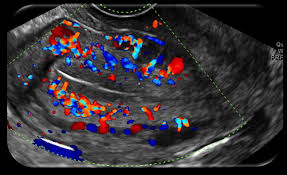

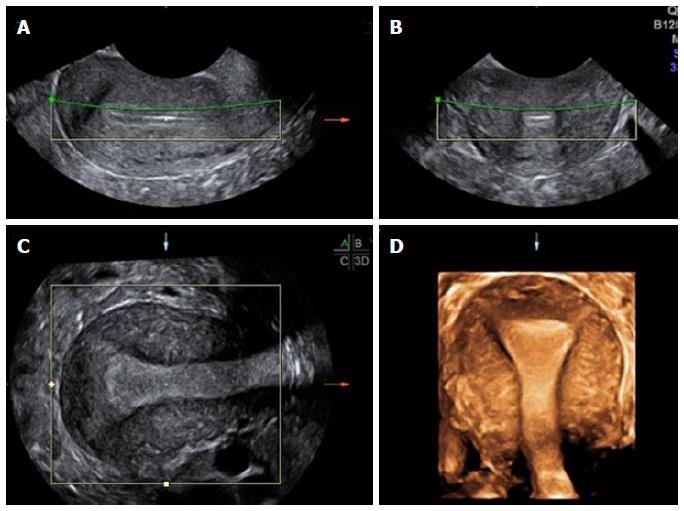
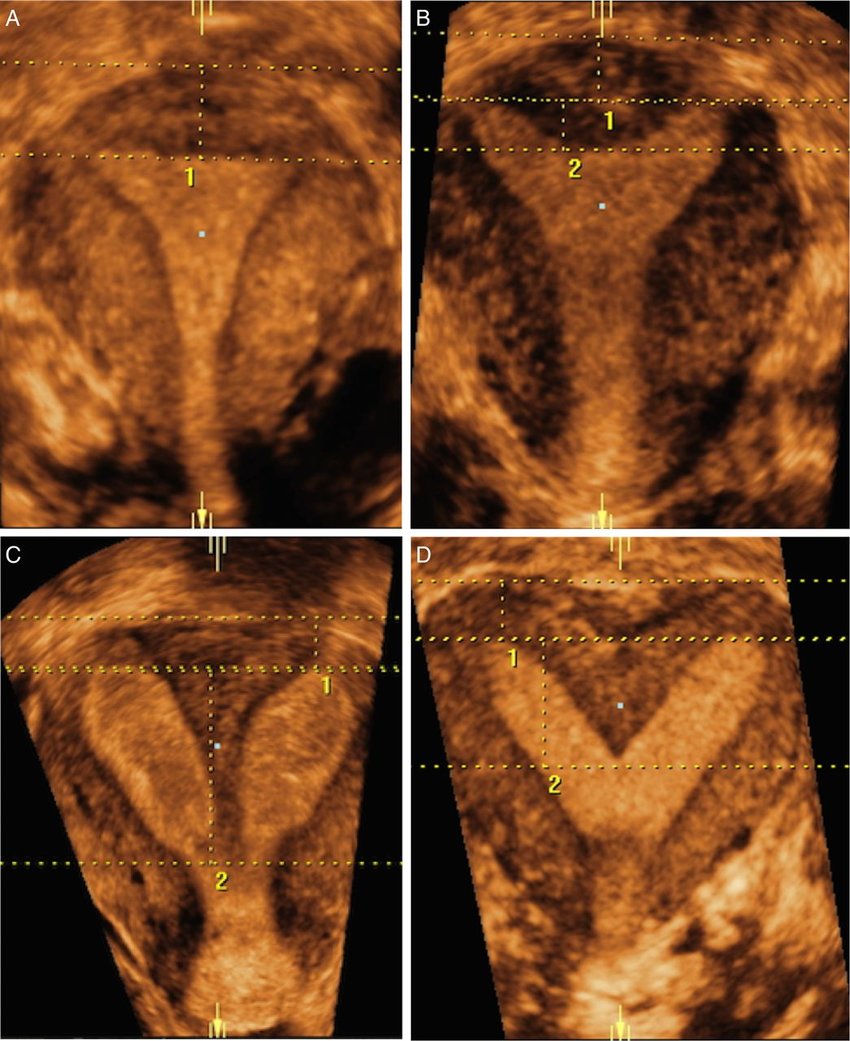
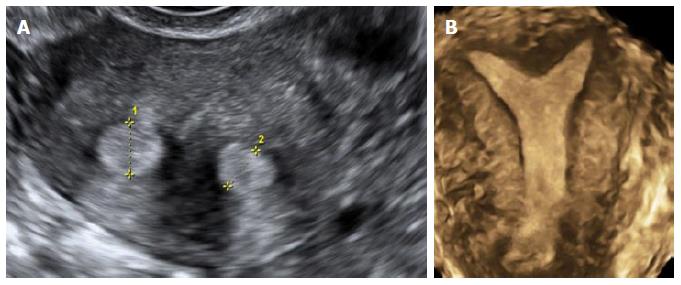
Apart from the location, mobility & size of the ovary, assessment of its volume & antral follicle count is also important to predict the outcome of any fertility therapy. Ovarian pathologies like functional cysts, PCO & endometriomas, tumors can be diagnosed by TVS.
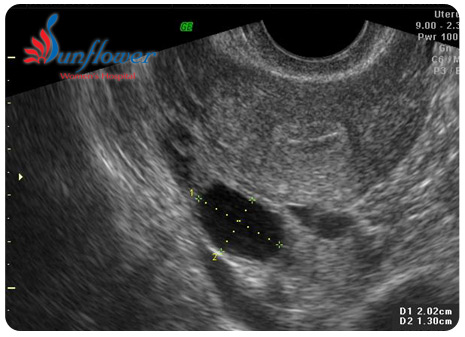

Healthy fallopian tubes are not visualized in a routine transvaginal scan (except if there is a massive fluid collection in the pelvis). Hence diagnosis of healthy tubes is a diagnosis of exclusion. But if fallopian tubes get infected and dilated (tuberculosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis) i.e. hydrosalpinx they can be visualise on TVS.
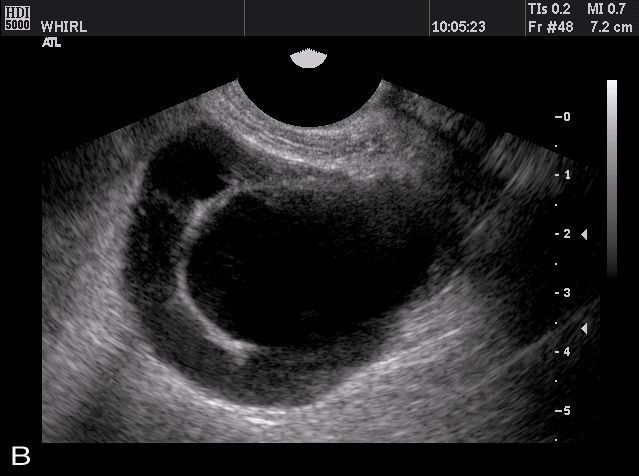
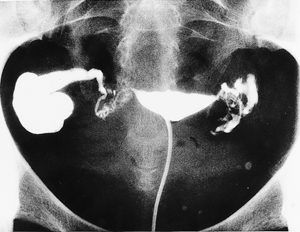

Excluding the periovulatory period, any free fluid in pelvis should be tried to diagnosed & treated before commencement of any treatment.
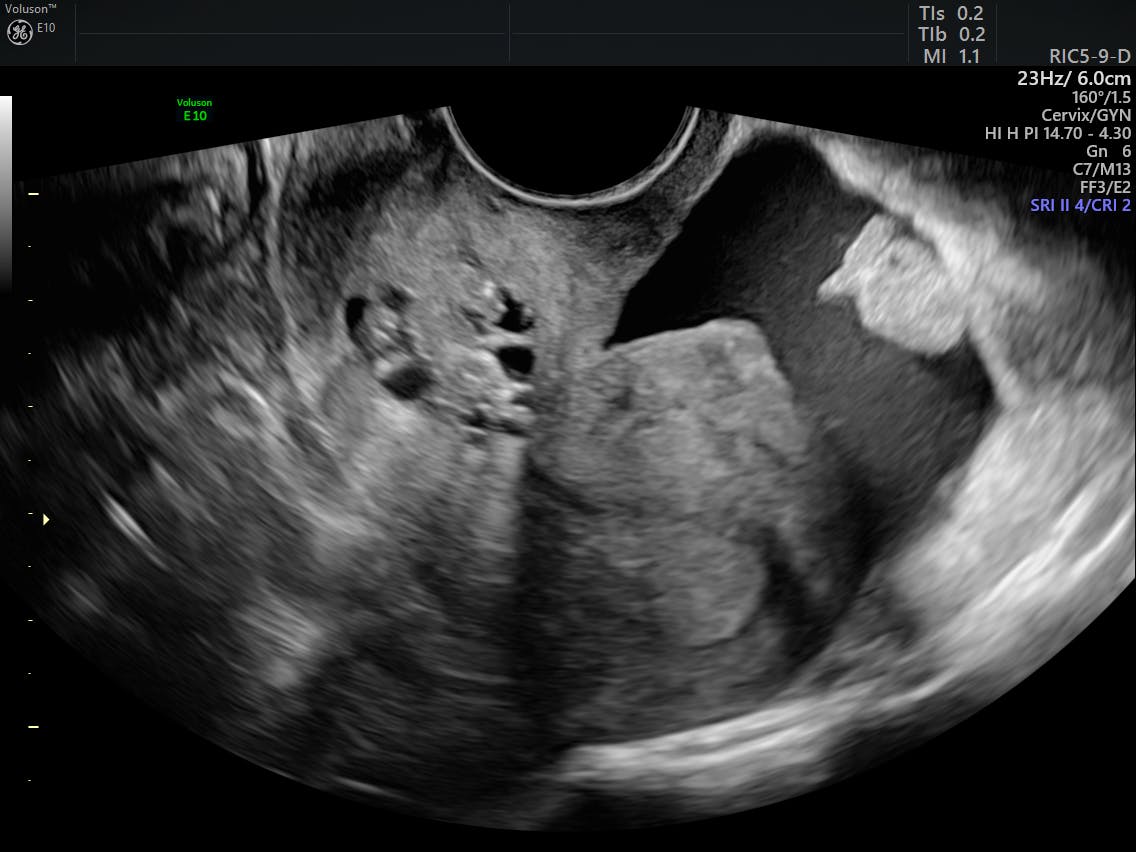
Ovarian Reserve
Women are born with all of the eggs that they will ever have, and they lose them constantly throughout life until menopause, when none remain. It would be helpful to have a reliable test that would tell us how many eggs a woman has remaining at a point in time – as well as telling us about the quality of those eggs. The term “ovarian reserve” is useful in the field of reproductive medicine. It is an estimate of the “reserve of the woman’s ovaries” – remaining egg supply – to be able to make babies in the future.
Female age is a very important consideration when estimating the probability for conception because it is a strong determinant of egg quality.
A 45 year old can have good quality eggs (for her age) and still be fertile, although this is rare. At the other extreme, a 25 year old can have very poor quality eggs and be infertile – unless she uses donor eggs. These are extreme examples, but the point is that egg quantity and quality tends to decline significantly in the midlle and late 30s and faster in the early 40s. Also, egg quantity and quality in an individual woman can be average for her age, better than average, or worse than average.
It would be nice to have a reliable test to determine how many eggs remain and how good the eggs are in an individual woman at a point in time. These tests are often referred to as tests of “ovarian reserve”.
Do ovarian reserve tests check egg quantity, quality , or both?
Ovarian reserve testing can tell us quite a lot about the remaining quantity of eggs a woman has, but it tells us very little about the quality of those eggs. Age is the best “test” that we have at this time for egg quality.
OVARIAN RESERVE TEST
Day 3 FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) and estradiol (E2) test
By measuring a baseline FSH on day 3 of the cycle, we can sometimes get an indication that the women is closer to menopause and has relatively less “ovarian reserve”. Another way of saying this is that if the baseline FSH is elevated the egg quantity is reduced from what is expected.
Anti-Mullerian hormone levels (AMH)
Blood levels of the hormone AMH are often used by fertility specialists as part of the evaluation of ovarian reserve.
Women with higher AMH values will tend to have better response to ovarian stimulation for IVF and have more eggs retrieved. In general, having more eggs with IVF gives a higher success rate.
AMH levels vary from laboratory to laboratory, but 2 to 4 ng/ml in the age group 18 to 30 years is considered normal.
AFC Antral Follicle Count
AFC is the number of follicles measuring 2-9 mm in both ovaries on trans vaginal sonography.
Normal AFC – 5-20
Poor response – < 5 PCOS(hyper responders) – > 24
FAQs
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) is one of the most important hormones involved in the natural menstrual cycle as well as in pharmacological (drug-induced) stimulation of the ovaries. It is the main hormone involved in producing mature eggs in the ovaries.
FSH is the same hormone that is contained in the injectable gonadotropins which are used to produce multiple eggs for infertility treatment.
Women in menopause usually have high FSH hormone levels that are above 40 mIU/ml. As women approach menopause their baseline FSH levels (day 3 of their cycle) will tend to gradually increase over the years.
By measuring a woman’s baseline FSH on day 3 of the cycle (we do it on day 2, 3, or 4), we get an indication as to whether she has normal “ovarian reserve”.
Therefore, if the baseline FSH is elevated the ovarian reserve (how many eggs are left) is reduced (sometimes the egg quality is also reduced).
A blood estradiol level on day 3 (we do it on any day between days 2 and 4) of the menstrual cycle is a way to potentially discover some of those women with a normal day 3 FSH that may in fact have decreased egg quantity and quality.
What we want on day three is a low FSH level in conjunction with a low estradiol level. If the FSH is normal but the estradiol level is elevated, the elevated estradiol will often be artificially “suppressing” the FSH level down to the normal range.
We like to see the day 3 estradiol less than about 80. In our clinic, levels of 80-100 are borderline, and over 100 are abnormal. We repeat borderline or abnormal results in another menstrual cycle to try to get a “true” FSH..
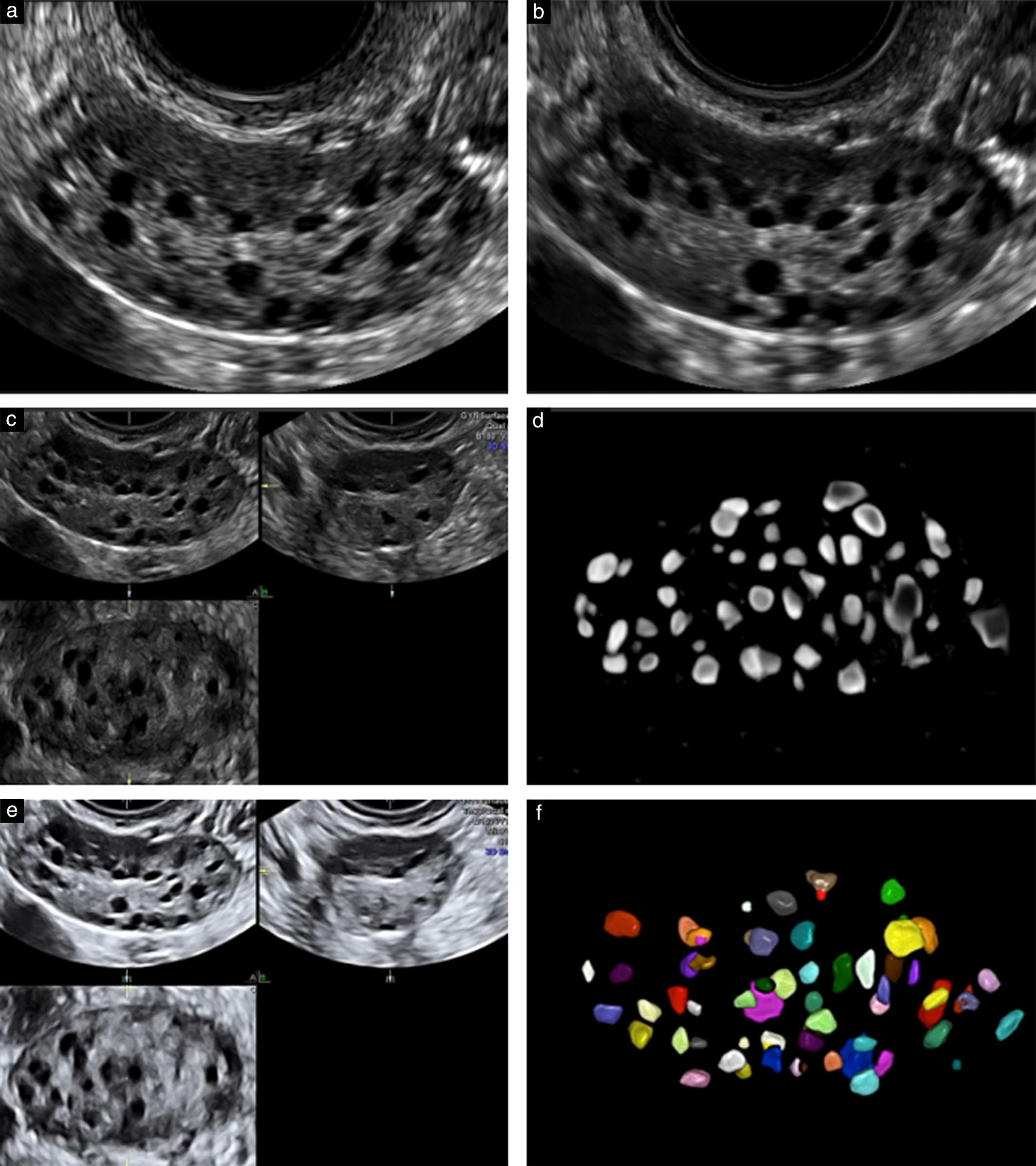
Antral follicles are small follicles (about 2-8 mm in diameter) that we can see – and measure and count – with ultrasound. Antral follicles are also referred to as resting follicles.
Vaginal ultrasound is the best way to accurately assess and count these small structures. In my opinion, the antral follicle counts (in conjunction with female age) are by far the best tool that we currently have for estimating ovarian reserve and/or chances for pregnancy with in vitro fertilization.
As women age, they have less eggs (primordial follicles) remaining, therefore they have fewer antral follicles on ultrasound.
- When there are an average (or high) number of antral follicles, we tend to get a “good” response with many mature follicles. We tend to get a good number of eggs at retrieval in these cases. Pregnancy rates are higher than average.
- When there are few antral follicles, we tend to get a poor response with few mature follicles. Cancellation of the IVF cycle is much more common when there is a low antral count. Pregnancy rates are lower overall in this group. The reduction in success rates is more pronounced in women over 35 years old.
- When the number of antral follicles is intermediate, the response is not as predictable. In most cases the response is intermediate. However, we could also have either a low or a good response when the antral counts are intermediate. Pregnancy rates are pretty good overall in this group.
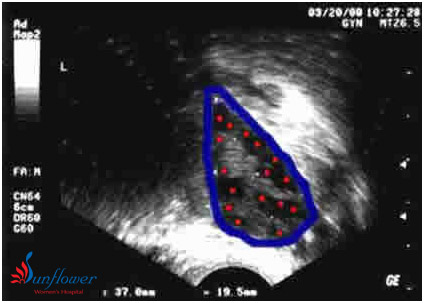
Ultrasound image of an ovary at the beginning of a menstrual cycle. No medications are being given. The ovary is outlined in blue. There are numerous antral follicles visible – marked with red spots. 16 are seen in this image, this ovary had a total of 35 antrals (only 1 plane is shown above) This is a polycystic ovary, with a high antral count and volume (ovary = 37 by 19.5mm) This woman had irregular periods and was a “high responder” to injectable FSH medication.
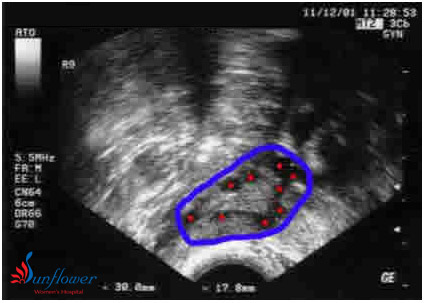
Ultrasound image of an ovary at the beginning of a menstrual cycle. No medications are being given. The ovary is outlined in blue. 9 antral follicles are seen – marked with red spots The ovary has normal volume (cursors measuring ovary = 30 by 17.8mm) This woman had regular periods and a normal response to injectable FSH drugs
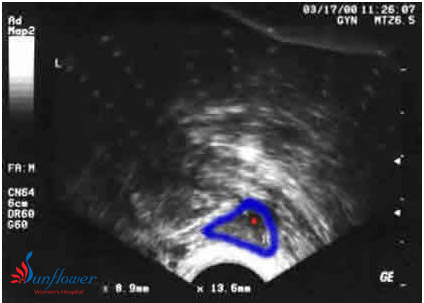
An ovary is outlined in blue and is small (low volume) with only 1 antral follicle. Her other ovary had only 2 antral follicles. She had regular periods and a normal day 3 FSH test. Attempts to stimulate her ovaries for IVF were not successful
There is not a perfect answer to this question. This means that if we had several different trained ultrasonographers do an antral count on a woman, they would not all get exactly the same result. 3-5 antral follicles would be indicative of good ovarian
Attempts to do IVF are sometimes “cancelled” when the ovaries respond very poorly to the stimulation meds because success rates are very low with less than 3 mature follicles.
There are no absolute and accepted cutoffs for defining “low”, “normal”, or “high-responders”. However, here are some general guidelines:
Low responder:– When stimulated aggressively with injectable FSH will develop less than 5 mature follicles – often requiring high doses of the medications. Some women will only develop 1 or 2 mature follicles – even on very high doses of the medications. These women are not good candidates for IVF using their own eggs – but are good candidates for in vitro fertilization with donor eggs.
“Normal” or “average” responder: When stimulated aggressively with injectable FSH will develop 5-8 mature follicles as well as several smaller ones.
High responder: When stimulated aggressively with injectables will develop about 8 or more mature follicles as well as many small and medium-sized follicles. These women usually respond briskly to lower doses of medications. They are at higher risk for ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
AMH, or anti-mullerian hormone is a substance that is produced by granulosa cells in ovarian follicles. The levels are quite constant and the AMH test can be done on any day of a woman’s cycle.
Since AMH is produced only in small ovarian follicles, blood levels of this substance have been used to attempt to measure the size of the pool of growing follicles in women.



